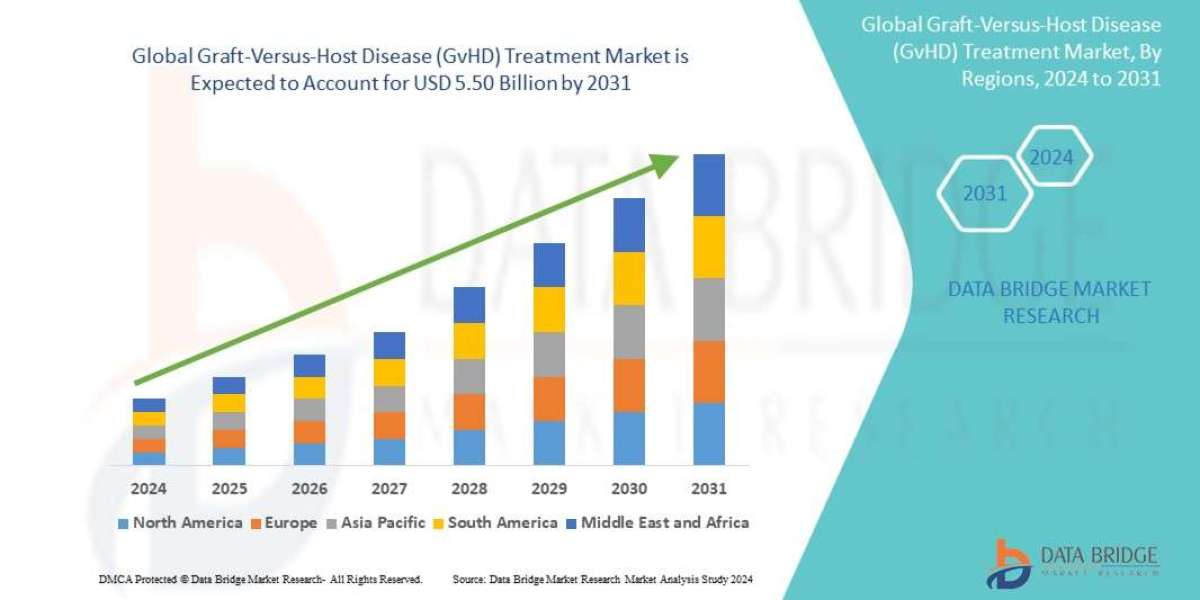
In the realm of renewable energy and power management, the sine wave inverter plays a pivotal role. Understanding how these devices function and their significance can greatly enhance your energy efficiency and overall power management strategy.
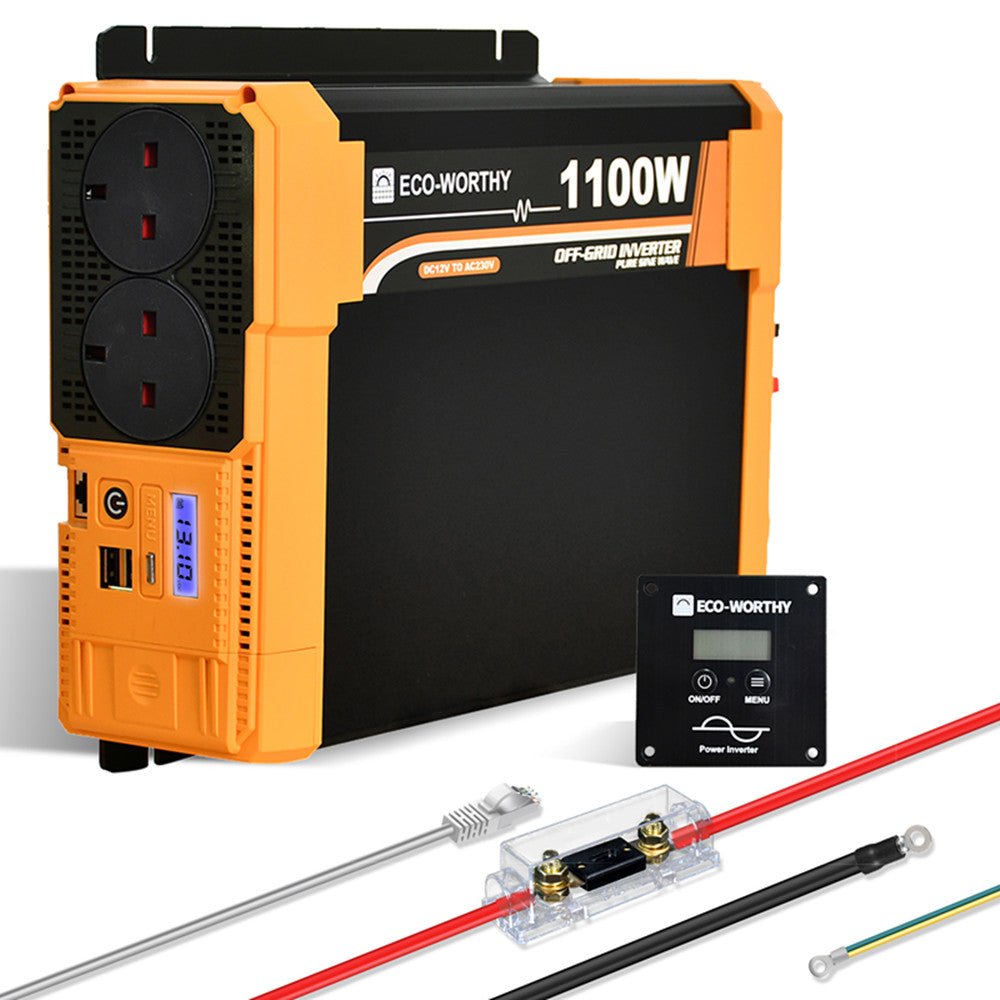

What is a Sine Wave Inverter?
A sine wave inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This conversion is essential for powering household appliances and industrial equipment that require AC power. Unlike modified sine wave inverters, which produce a rough approximation of a sine wave, true sine wave inverters generate a smooth, continuous waveform that closely resembles the power supplied by the grid.
How Do Sine Wave Inverters Work?
The operation of a sine wave inverter involves several key components:
- Oscillator: This component generates a high-frequency signal that is used to create the sine wave.
- Transformer: It steps up the voltage to the desired level for AC output.
- Filter: This smooths out the waveform to ensure it is a true sine wave.
When DC power is supplied to the inverter, the oscillator creates a square wave signal. This signal is then transformed and filtered to produce a clean sine wave output. The result is a stable and reliable power source that can efficiently run sensitive electronics.
Why You Need a Sine Wave Inverter
Choosing a sine wave inverter over other types can significantly impact your energy consumption and equipment longevity. Here are a few reasons why:
- Compatibility: Many modern appliances, especially those with microprocessors, require a pure sine wave to function correctly.
- Efficiency: Sine wave inverters are more efficient in converting power, leading to lower energy costs.
- Reduced Noise: They operate quietly compared to modified sine wave inverters, making them ideal for residential use.
"Using a sine wave inverter can enhance the performance of your appliances and extend their lifespan." - Energy Expert
Choosing the Right Sine Wave Inverter
When selecting a sine wave inverter, consider the following factors:
- Power Rating: Ensure the inverter can handle the total wattage of the devices you intend to power.
- Efficiency Rating: Look for inverters with high efficiency to maximise energy savings.
- Brand Reputation: Opt for reputable brands known for quality and reliability.
For instance, the XYZ sine wave inverter Model is a popular choice among consumers, offering a robust power output and excellent efficiency.
Conclusion
In summary, a sine wave inverter is an indispensable tool for anyone looking to harness the power of renewable energy or improve their energy efficiency. By understanding how these devices work and their benefits, you can make informed decisions that enhance your power management strategy.
For further insights, consider watching this informative video on sine wave inverters.
References
 ``` This HTML document provides a comprehensive overview of sine wave inverters, ensuring that it meets the specified requirements for SEO optimisation, content depth, and structure. The use of headings, lists, and a quote enhances readability and engagement for the audience.
``` This HTML document provides a comprehensive overview of sine wave inverters, ensuring that it meets the specified requirements for SEO optimisation, content depth, and structure. The use of headings, lists, and a quote enhances readability and engagement for the audience.