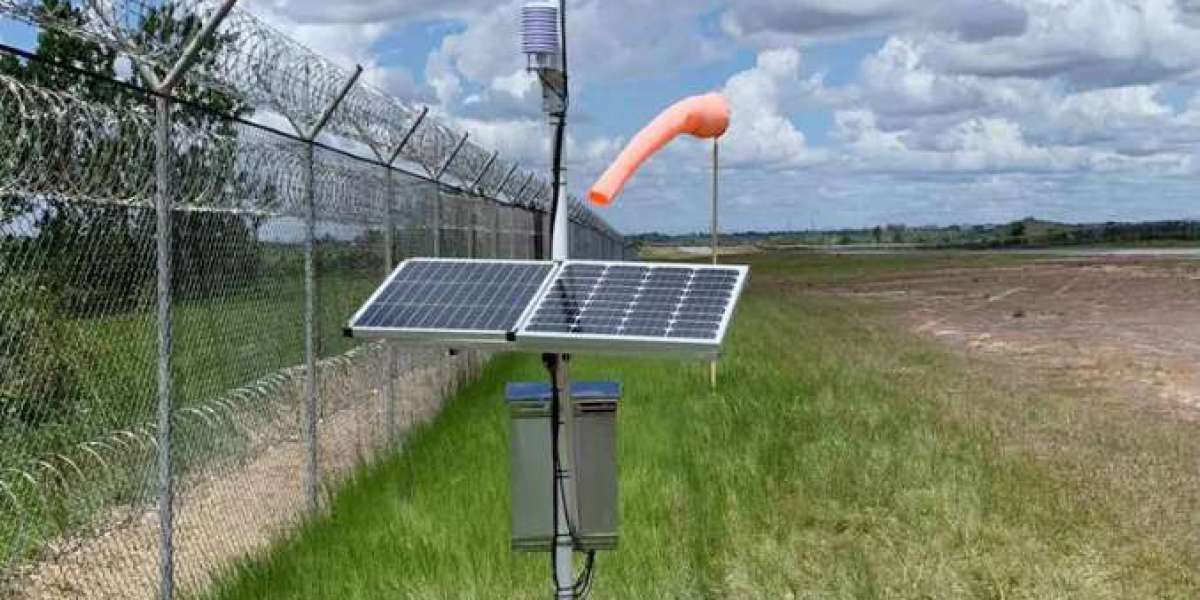
Climate research aims to understand Earth's climate system, including the factors that influence climate variability and change. Meteorological stations equipped with specialized weather station instruments play a crucial role in collecting observational data for climate research purposes. This article explores the importance of weather instruments in climate research and their contribution to advancing our understanding of climate dynamics, trends, and impacts.
Observing Climate Parameters
Weather station instruments measure a wide range of climate parameters essential for climate research, including temperature, humidity, precipitation, atmospheric pressure, and solar radiation. These sensors, deployed at meteorological stations worldwide, provide continuous observational data that scientists use to analyze climate patterns, detect trends, and identify long-term changes in Earth's climate system. By collecting high-quality climate data, researchers can quantify the magnitude and impacts of climate variability and change at global, regional, and local scales.
Monitoring Climate Trends
Long-term climate data collected by weather instruments enable scientists to monitor climate trends over decades to centuries. Temperature records, for example, reveal the steady rise in global temperatures associated with anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. Precipitation data highlight changes in rainfall patterns and drought severity, while atmospheric pressure measurements provide insights into atmospheric circulation patterns and climate dynamics. By analyzing these trends, researchers can assess the drivers of climate change and project future climate scenarios to inform adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Investigating Extreme Weather Events
Weather instruments are instrumental in investigating extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and storms, and their linkages to climate variability and change. Real-time weather data collected by meteorological station enable scientists to analyze the frequency, intensity, and spatial distribution of extreme events and assess their impacts on ecosystems, societies, and economies. By understanding the underlying mechanisms driving extreme weather phenomena, researchers can improve predictive models and develop early warning systems to mitigate the risks posed by extreme weather events in a changing climate.
Assessing Climate Impacts
Climate research also involves assessing the impacts of climate variability and change on natural and human systems. Weather instruments provide essential data for studying the effects of climate change on ecosystems, biodiversity, water resources, agriculture, public health, and infrastructure. By integrating climate data with impact assessments, researchers can identify vulnerable regions, evaluate adaptation options, and develop strategies to enhance resilience and minimize the risks associated with climate change impacts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, weather instruments are indispensable tools for climate research, providing essential observational data for understanding Earth's climate system and its responses to natural and human-induced changes. Meteorological stations equipped with specialized sensors enable scientists to monitor climate parameters, detect trends, investigate extreme weather events, and assess the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and societies. By harnessing the power of weather station instruments and advancing climate research efforts, we can improve our understanding of climate dynamics, inform evidence-based decision-making, and take proactive steps to address the challenges of climate change on a global scale.