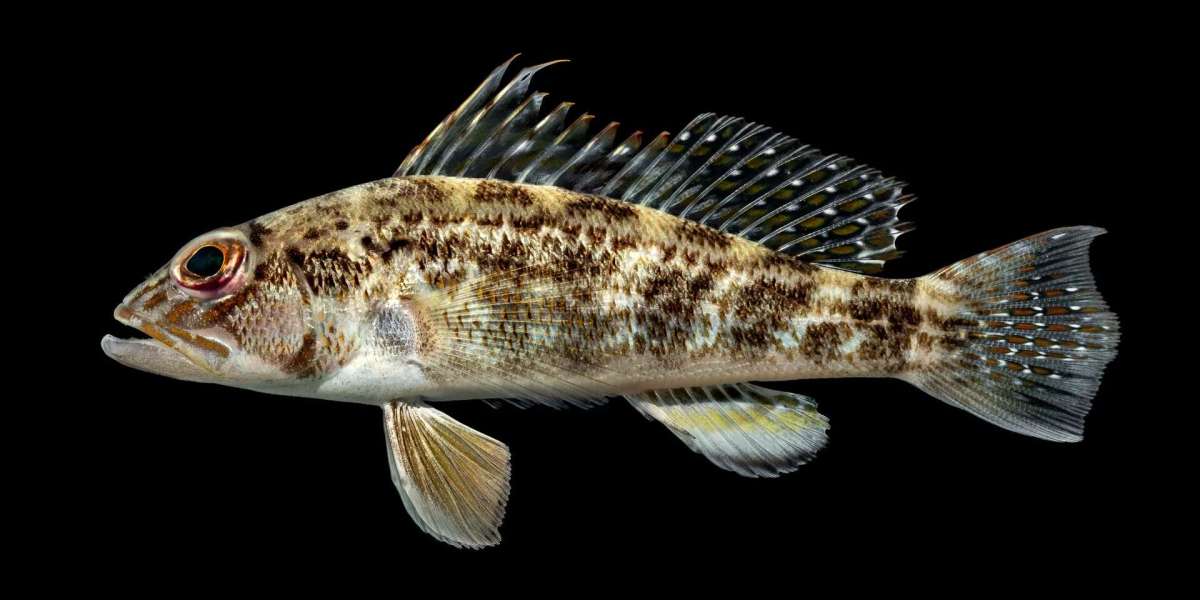
White seabass Fish (Atractoscion nobilis) is a species of fish in the Sciaenidae family, widely valued for both commercial and recreational fishing. They are found primarily in the eastern Pacific Ocean, along the coast from Alaska to the Baja California peninsula. To support conservation efforts and enhance fishing management, it is important to understand the habitat preferences of white seabass. Here, we explore the various aspects of their preferred environments including geographical location, water conditions, and habitat types.
Geographic Range
White seabass are primarily found along the Pacific coast of North America. Their range extends from the Gulf of Alaska down to southern Baja California. However, they are most commonly seen off the coast of California, especially from Point Conception to San Diego. This fish species has shown some migratory behaviors, often moving in response to changes in water temperature and prey availability.
Water Conditions
White seabass prefer marine environments with water temperatures ranging from about 50°F to 70°F (10°C to 21°C). They are usually found in nearshore waters but can also be found at depths of up to 300 feet. The fish are particularly sensitive to the conditions of the water, preferring areas with good water clarity and moderate currents which help in the distribution of their primary food sources.
Habitat Types
1. Kelp Forests
- White seabass frequently inhabit kelp forests, which provide abundant food and protection from predators. Kelp forests offer a complex structure that supports a rich biodiversity, including many of the smaller fish and invertebrates that white seabass prey upon.