In the realm of construction and renovation, core drills are indispensable tools for creating precise holes in various materials such as concrete, stone, and masonry. Among the plethora of core drills available in the market, two primary types stand out. handheld core drills and larger, stationary core drills. Both serve the same purpose but offer distinct features and capabilities. The comparison between Handheld Core Drills and stationary core drills, exploring their differences, advantages, and applications.
Size and Portability:
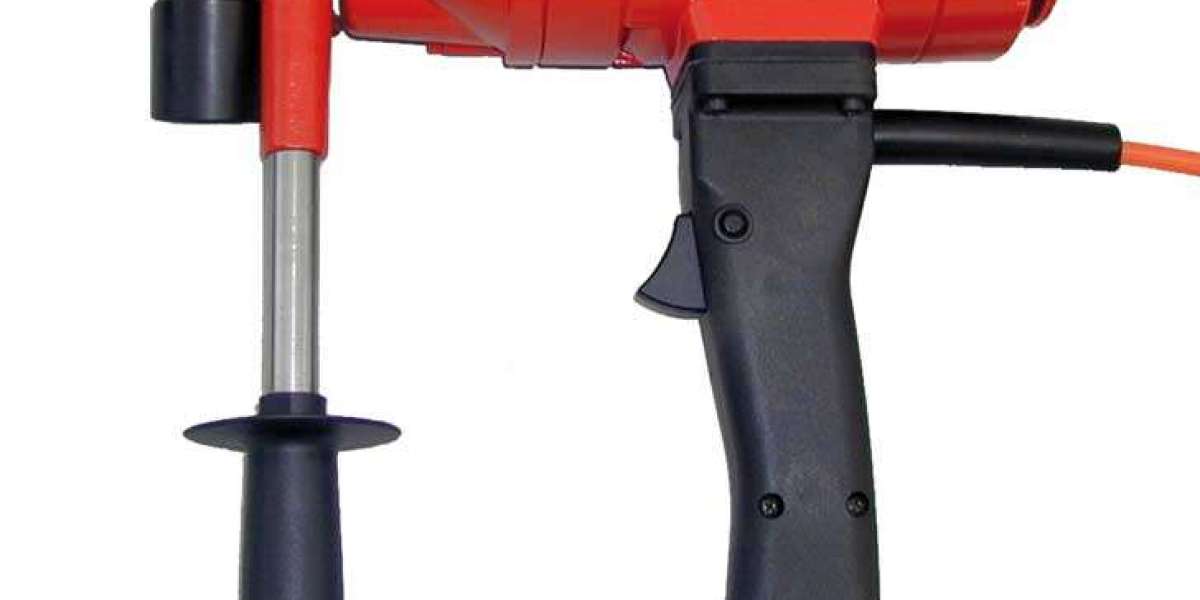
Handheld Core Drills
Handheld core drills are prized for their compact size and portability. They are designed to be lightweight and easy to maneuver, making them ideal for tasks that require mobility and access to tight spaces. Construction professionals and contractors often favor handheld core drills for on-the-go projects or jobs that demand versatility.
Stationary Core Drills
In contrast, stationary core drills are bulkier and typically mounted on a stand or base. While they lack the portability of handheld models, stationary core drills excel in stability and precision. They are well-suited for large-scale projects where consistent hole depth and accuracy are paramount, such as drilling multiple holes in a concrete slab or wall.
Power and Performance:
Handheld Core Drills
Despite their smaller size, handheld core drills pack a punch in terms of power and performance. Modern handheld models are equipped with high-torque motors and advanced drilling mechanisms that allow them to tackle tough materials with ease. Additionally, some handheld core drills feature variable speed settings and ergonomic designs for enhanced control and efficiency.
tationary Core Drills
Stationary core drills, on the other hand, boast robust motors and heavy-duty construction. They are capable of generating immense drilling force and maintaining consistent speed and torque throughout prolonged use. This makes stationary core drills well-suited for demanding applications that require deep, precise holes in tough materials.
Versatility and Accessibility:
Handheld Core Drills
One of the primary advantages of handheld core drills is their versatility. They can be used in a wide range of applications, from plumbing and electrical work to HVAC installation and general construction. Handheld core drills are also highly accessible, allowing operators to easily switch between drilling positions and angles without the need for complex setup or adjustment.
Stationary Core Drills
While stationary core drills excel in stability and precision, they are somewhat limited in terms of versatility. Due to their fixed position on a stand or base, stationary core drills are best suited for tasks that require consistent drilling angles and depths. They are commonly used in industrial settings and large-scale construction projects where accuracy and efficiency are paramount.
Cost and Investment:
Handheld Core Drills
Handheld core drills are generally more affordable than their stationary counterparts, making them an attractive option for contractors and DIY enthusiasts on a budget. Additionally, the lower upfront cost of handheld core drills may appeal to small-scale operators or those who only require occasional use of the tool.
- Stationary Core Drills
Stationary core drills represent a significant investment, both in terms of upfront cost and long-term maintenance. However, for professionals and contractors who regularly undertake large-scale drilling projects, the superior performance and reliability of stationary core drills justify the initial investment. Moreover, stationary core drills often come with extended warranties and support services to ensure maximum uptime and productivity.
Application and Use Cases:
Handheld Core Drills
Handheld core drills excel in applications that demand flexibility, mobility, and accessibility. They are commonly used for tasks such as installing plumbing fixtures, creating electrical conduit openings, and performing small-scale concrete repairs. Handheld core drills are also popular in industries such as landscaping, where precision drilling is required in tight or hard-to-reach spaces.
Stationary Core Drills
Stationary core drills are indispensable tools for large-scale construction projects, infrastructure development, and industrial applications. They are frequently used in tasks such as drilling anchor holes, creating ventilation openings, and cutting through reinforced concrete structures. Stationary core drills are also preferred for projects that require high-volume drilling or repetitive hole patterns, thanks to their stability and consistency.
Conclusion:
Both Handheld Core Drills and stationary core drills offer unique advantages and capabilities that cater to different needs and preferences. Handheld core drills are prized for their portability, versatility, and affordability, making them ideal for small-scale projects and tasks that require mobility and flexibility. On the other hand, stationary core drills excel in stability, precision, and performance, making them indispensable tools for large-scale construction projects and industrial applications. Ultimately, the choice between handheld and stationary core drills depends on factors such as project requirements, budget constraints, and personal preferences. By understanding the differences and applications of each type of core drill, contractors and DIY enthusiasts can make informed decisions to achieve optimal results in their drilling endeavors.