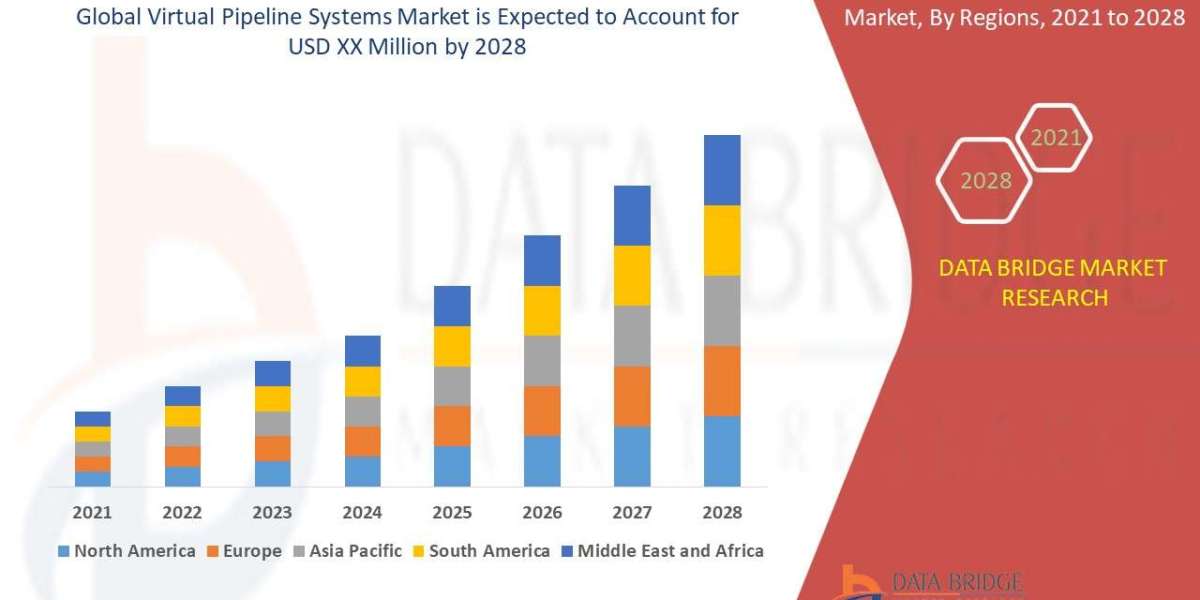
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. This condition is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Understanding ADHD is crucial for effective management and support.

Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
The symptoms of ADHD can vary significantly among individuals. Generally, they are categorized into two main types: inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity. Here are some common symptoms:
- Inattention: Difficulty sustaining attention in tasks, frequent careless mistakes, and trouble organizing activities.
- Hyperactivity: Fidgeting, excessive talking, and difficulty remaining seated in situations where it is expected.
- Impulsivity: Interrupting others, difficulty waiting for one's turn, and making hasty decisions without considering the consequences.
Diagnosis of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Diagnosing ADHD involves a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional. This process typically includes:
- A detailed history of the individual's behavior and symptoms.
- Standardized rating scales and questionnaires completed by parents, teachers, or caregivers.
- A thorough physical examination to rule out other medical conditions.
It is essential to note that ADHD can often co-occur with other disorders, such as anxiety and learning disabilities. Therefore, a multifaceted approach to diagnosis is vital.
Treatment Options for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Effective treatment for ADHD often includes a combination of behavioral therapies, educational support, and medication. Here are some common treatment options:
- Behavioral Therapy: This approach focuses on modifying specific behaviors and developing coping strategies.
- Medication: Stimulants, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, are commonly prescribed to help manage symptoms.
- Educational Support: Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) or 504 Plans can provide accommodations in school settings.
For more insights into ADHD and its similarities and differences with other conditions, you can explore this detailed comparison.
Conclusion
Understanding attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is essential for fostering a supportive environment for those affected. By recognizing the symptoms, pursuing accurate diagnosis, and exploring effective treatment options, individuals with ADHD can lead fulfilling lives. If you suspect that you or someone you know may have ADHD, consider seeking professional guidance to navigate this complex condition.