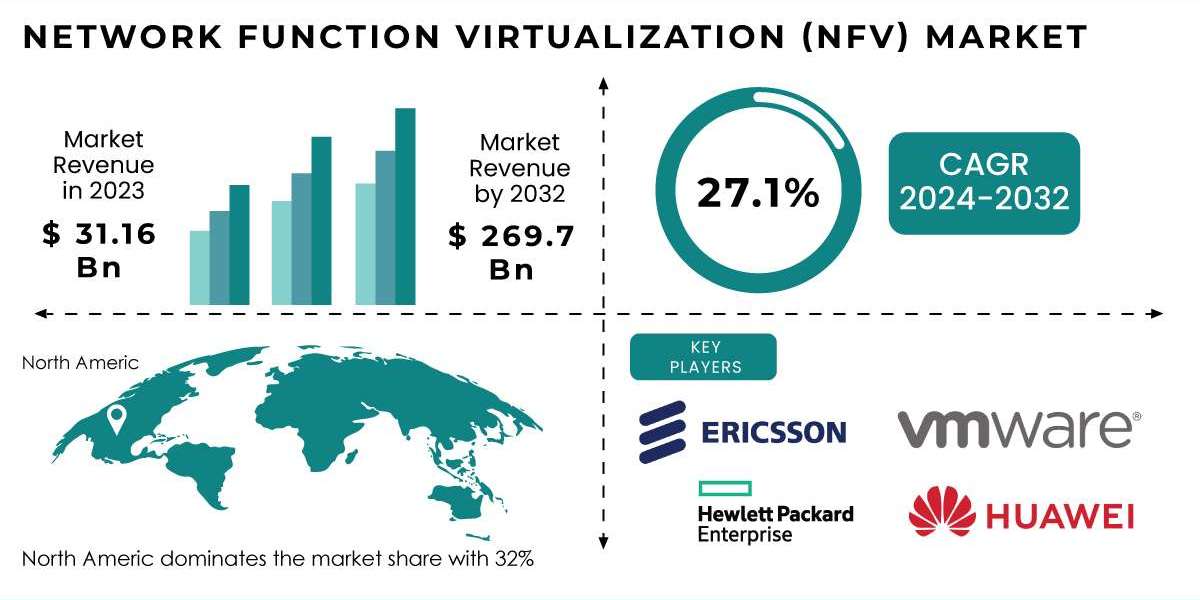
Network Function Virtualization 2024
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is a transformative approach that redefines how network services are delivered and managed. By decoupling network functions from dedicated hardware appliances and implementing them as virtualized instances on standardized hardware, NFV allows for more agile and flexible network operations. This shift not only optimizes resource utilization but also enhances scalability, enabling organizations to quickly adapt to changing demands. The growing importance of NFV is underscored by its significant impact on the telecommunications industry, where it has led to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. The Network Function Virtualization Market Share reflects this trend, as organizations recognize the potential benefits of adopting NFV strategies in their network infrastructure.
The rise of NFV is driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for cost-effective and scalable networking solutions, the need for greater flexibility in service deployment, and the shift towards cloud-based architectures. Traditional networking methods often involve dedicated hardware for each function—such as firewalls, routers, and load balancers—leading to complex management and high capital expenditures. NFV addresses these challenges by allowing multiple virtual network functions (VNFs) to run on a single hardware platform, facilitating centralized management and reducing hardware reliance. This shift not only lowers costs but also enhances agility, enabling service providers to introduce new services rapidly and efficiently.
Key Components of NFV
At the heart of NFV are several critical components that work together to deliver a robust virtualized networking environment. These components include virtualization infrastructure, network function virtualization orchestrators (NFVOs), virtualized network functions (VNFs), and management and orchestration (MANO) systems.
The virtualization infrastructure forms the foundation of NFV, comprising the physical hardware—such as servers, storage, and networking equipment—along with the hypervisor that enables the creation and management of virtual machines. This infrastructure allows service providers to run multiple VNFs on common hardware, maximizing resource utilization and reducing costs.
Network function virtualization orchestrators (NFVOs) play a pivotal role in managing the lifecycle of VNFs. They handle the deployment, scaling, and orchestration of VNFs across the virtualized environment, ensuring that network functions are efficiently allocated and optimized for performance. NFVOs enable service providers to automate network operations, reducing manual intervention and the risk of human error.
Virtualized network functions (VNFs) are the software-based instances that replace traditional hardware-based networking appliances. VNFs can include a wide range of network services, such as virtual routers, firewalls, and load balancers. By implementing these functions in software, service providers gain greater flexibility and can rapidly deploy or update services without the need for physical hardware changes.
Management and orchestration (MANO) systems provide the necessary tools to oversee the entire NFV ecosystem. They integrate the various components, facilitating coordination and communication between VNFs, NFVOs, and the underlying infrastructure. MANO systems also enable monitoring, analytics, and fault management, ensuring that the virtualized network operates smoothly and efficiently.
Benefits of Network Function Virtualization
One of the most significant advantages of NFV is its ability to reduce costs. By eliminating the need for dedicated hardware for each network function, organizations can save on capital expenditures while also minimizing operational expenses. The ability to use commodity hardware further drives down costs, as organizations can leverage existing infrastructure to support NFV deployments.
NFV also enhances network agility and flexibility. Traditional networking setups often require lengthy deployment cycles for new services, which can hinder a service provider's ability to respond to market demands. NFV allows for rapid provisioning and scaling of network functions, enabling service providers to quickly launch new services or modify existing ones. This agility is particularly crucial in an increasingly competitive landscape where time-to-market can determine success.
Moreover, NFV promotes improved scalability. Organizations can dynamically scale VNFs based on demand, allowing them to allocate resources efficiently during peak usage periods and scale down when demand decreases. This scalability ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness, as resources are used only when necessary.
The increased automation capabilities that NFV offers also lead to improved operational efficiency. By automating routine tasks, such as provisioning, monitoring, and scaling, organizations can reduce manual workloads, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. Automation not only speeds up operations but also reduces the risk of errors associated with manual interventions.
Challenges of Implementing NFV
Despite its numerous benefits, the implementation of NFV is not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is interoperability. As organizations adopt NFV, they often work with multiple vendors and technologies, leading to potential compatibility issues. Ensuring that different VNFs can seamlessly communicate and operate together is crucial for the success of NFV deployments.
Another challenge lies in the management and orchestration of virtualized environments. The complexity of managing numerous VNFs and ensuring their performance requires sophisticated orchestration tools and processes. Organizations must invest in the right technologies and skill sets to effectively manage NFV ecosystems and maximize their benefits.
Security is also a significant consideration in NFV deployments. Virtualized environments can introduce new vulnerabilities, as the software-based nature of VNFs can be more susceptible to cyberattacks compared to traditional hardware-based solutions. Organizations must implement robust security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and continuous monitoring, to safeguard their virtualized networks.
Furthermore, organizations may face cultural and organizational resistance when transitioning to NFV. The shift from traditional networking approaches to NFV requires a change in mindset and operational processes. IT teams may need training and support to adapt to new technologies and workflows, which can slow down the adoption process.
Future Trends in Network Function Virtualization
As the NFV landscape continues to evolve, several trends are shaping its future. One notable trend is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into NFV environments. These technologies can enhance automation capabilities, enabling more intelligent decision-making and resource allocation. AI-driven analytics can also provide insights into network performance, helping organizations proactively address issues and optimize operations.
The rise of edge computing is another trend that will impact NFV. With the growing demand for low-latency applications and services, organizations are increasingly deploying VNFs closer to the edge of the network. This allows for faster processing and reduced latency, enabling applications such as IoT and real-time analytics to thrive.
Moreover, the transition to 5G networks will further accelerate the adoption of NFV. 5G networks require flexible and scalable architectures to support a wide range of applications, from autonomous vehicles to smart cities. NFV provides the necessary foundation to meet these demands, making it a critical component of future 5G deployments.
Conclusion
Network Function Virtualization represents a significant advancement in network management, offering organizations the opportunity to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance service delivery. By virtualizing network functions and leveraging automation, organizations can create agile, scalable, and efficient networking environments that meet the demands of today's digital landscape. While challenges remain in the implementation of NFV, the benefits it provides make it a compelling solution for service providers looking to stay competitive in an increasingly dynamic market. As NFV continues to evolve and integrate with emerging technologies, it is poised to play a vital role in shaping the future of networking.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)
About Us
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Read Our Other Reports:
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Market Report