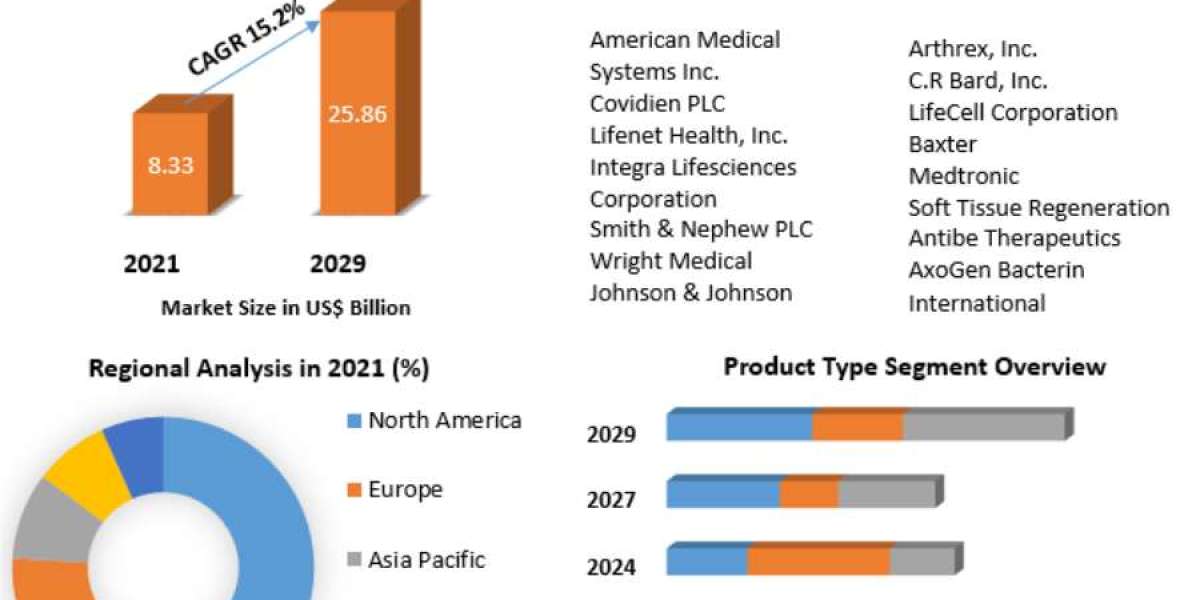
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and pervasive, traditional security models are often inadequate. As organizations strive to protect sensitive data and ensure seamless operations, a paradigm shift in cybersecurity has emerged: Zero Trust Security. This model, built on the premise of “never trust, always verify,” is reshaping how companies approach security. Zero trust security vendors are at the forefront of this transformation, offering solutions that redefine protection mechanisms for modern enterprises.
Understanding Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is a concept that eliminates the assumption of trust within a network. Unlike traditional security models that rely on perimeter defenses, zero trust assumes that threats can exist both inside and outside the network. Therefore, every access request, whether originating from inside or outside the network, is verified and authenticated before access is granted. This model hinges on several core principles:
- Least Privilege Access: Users and devices are given the minimum levels of access necessary to perform their functions.
- Micro-Segmentation: The network is divided into smaller segments to limit lateral movement of threats.
- Continuous Monitoring and Validation: Security systems continuously monitor and validate user activities and access requests.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA is implemented to ensure that users are who they claim to be.
- Assumption of Breach: Security strategies are designed with the assumption that a breach has already occurred, focusing on containment and minimizing damage.
Key Players in the Zero Trust Security Market
Several vendors have emerged as leaders in the zero trust security space, each offering unique solutions and capabilities. These vendors provide a range of tools and services designed to implement and enhance zero trust architectures. Here are some of the prominent players:
- Palo Alto Networks: Known for its comprehensive cybersecurity solutions, Palo Alto Networks offers a zero trust architecture that integrates network, cloud, and endpoint security. Their approach emphasizes continuous monitoring, policy enforcement, and automated threat response.
- Zscaler: A cloud-native security platform, Zscaler offers zero trust network access (ZTNA) solutions that provide secure, direct connectivity for users to applications, regardless of their location. Zscaler’s approach focuses on minimizing the attack surface and ensuring secure access to internal applications.
- Okta: Specializing in identity and access management, Okta plays a crucial role in zero trust implementations. Their platform provides secure authentication and authorization, with robust MFA and single sign-on (SSO) capabilities, ensuring that only verified users can access sensitive resources.
- Cisco: Cisco’s zero trust solutions encompass network, endpoint, and cloud security. Their offerings include Cisco SecureX, which provides visibility and automated response capabilities across the entire security infrastructure, and Cisco Duo, which delivers strong MFA and device trust verification.
- Microsoft: Leveraging its extensive ecosystem, Microsoft integrates zero trust principles across its products and services. Microsoft Azure’s zero trust architecture includes identity protection, device compliance, and adaptive access controls, ensuring a holistic approach to security.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
Adopting a zero trust security model brings numerous benefits to organizations, enhancing their overall security posture and resilience against cyber threats. Some of the key advantages include:
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: By continuously verifying every access request and minimizing the attack surface, zero trust significantly reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Enhanced Visibility and Control: Zero trust provides comprehensive visibility into network activities and user behaviors, enabling organizations to detect and respond to threats more effectively.
- Improved Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks and standards now emphasize the need for robust access controls and continuous monitoring, which are core components of zero trust security.
- Increased Agility and Scalability: Zero trust solutions, particularly those that are cloud-based, offer the flexibility and scalability needed to adapt to changing business needs and evolving threats.
Challenges and Considerations
While zero trust security offers compelling advantages, its implementation can be challenging. Organizations must consider several factors to ensure a successful deployment:
- Cultural Shift: Transitioning to a zero trust model requires a cultural shift within the organization, with a focus on security awareness and training.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Zero trust solutions must integrate seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure and security tools to avoid disruption and maximize effectiveness.
- Cost and Complexity: Implementing zero trust can involve significant upfront costs and complexity, particularly for large organizations with diverse IT environments.
- Continuous Management: Zero trust is not a one-time implementation but requires ongoing management, monitoring, and policy adjustments to remain effective.
The Future of Zero Trust Security
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the adoption of zero trust security is expected to accelerate. The shift towards remote work and cloud computing has further underscored the need for robust, adaptive security models that can protect distributed environments. Zero trust vendors are likely to continue innovating, developing more advanced solutions that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
In conclusion, zero trust security represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. By focusing on continuous verification, least privilege access, and comprehensive monitoring, zero trust vendors are helping businesses protect their most valuable assets in an increasingly complex threat landscape. As the digital world evolves, zero trust will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of cybersecurity.