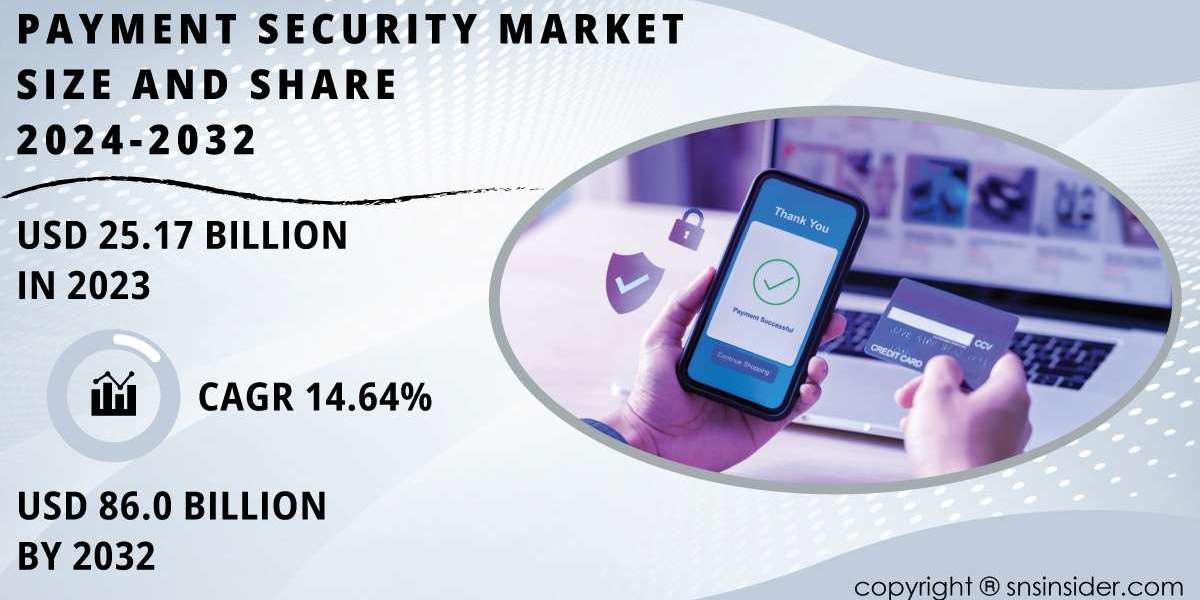
Payment Security 2024
As digital transactions become an essential part of daily life, the demand for secure payment systems has reached unprecedented levels. From e-commerce purchases to peer-to-peer money transfers, payment security plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and privacy of sensitive financial data. As more consumers and businesses embrace digital payment solutions, the risks associated with cyber threats, fraud, and data breaches have surged, emphasizing the importance of robust security measures. This growing concern over online payment security has led to significant investments and innovations in the field. The Payment Security Market Share has been on a steady rise, driven by the increasing need for sophisticated solutions to protect transactions. In 2023, the Payment Security Market was valued at USD 25.17 billion, and it is projected to reach USD 86 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.64% over the forecast period of 2024-2032.
Payment security involves a variety of technologies and protocols designed to safeguard sensitive information during financial transactions. Whether it's credit card details, personal identification numbers (PINs), or other financial data, ensuring that this information is securely transmitted and stored is vital to preventing unauthorized access or theft. With the rise of online shopping, mobile payments, and contactless technologies, businesses are under immense pressure to implement advanced security systems to protect their customers' information and maintain trust. From encryption to tokenization, modern payment security measures are continually evolving to keep pace with emerging threats.
The Core Components of Payment Security
At the heart of payment security are several key technologies and practices designed to protect financial data at every stage of a transaction. One of the most critical components is encryption. Encryption works by converting sensitive information into a code, which can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key. This ensures that even if cybercriminals intercept the data, they cannot access the underlying information. Payment encryption typically occurs in two primary stages: during transmission (as the data is sent over a network) and while the data is at rest (stored in a database or payment system).
Another critical element of payment security is tokenization. Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with a non-sensitive token that can be used to authorize a transaction without exposing actual account information. This technique is especially beneficial for preventing data breaches, as it ensures that even if a system is compromised, the stolen data cannot be used to carry out fraudulent transactions. Tokenization is commonly used in mobile payments and online purchases, offering a robust layer of protection for cardholders.
Secure payment authentication mechanisms also play a pivotal role in payment security. Techniques such as two-factor authentication (2FA) and biometric verification, including fingerprint or facial recognition, add an extra layer of security to the transaction process. These methods make it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access accounts, even if they obtain login credentials or payment details.
Regulatory and Compliance Landscape
As payment security becomes more critical, so does the regulatory environment surrounding it. Governments and financial institutions worldwide have implemented stringent rules and standards to ensure that businesses adhere to best practices for protecting financial data. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is one such framework. PCI DSS establishes a set of security requirements for companies that process, store, or transmit credit card information. Compliance with PCI DSS is mandatory for businesses operating in the payment industry and includes guidelines on encryption, access control, and network security.
In addition to PCI DSS, many countries have introduced regulations that address data privacy and protection more broadly. For example, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates how businesses must handle the personal data of EU citizens, including financial information. Similarly, in the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) provides consumers with rights over how their data is collected, stored, and used by businesses.
For organizations, compliance with these regulations is not only about avoiding hefty fines but also about maintaining customer trust. Data breaches and payment fraud can have severe consequences for businesses, including reputational damage and loss of customer confidence. As a result, many companies are prioritizing payment security measures that exceed regulatory requirements to minimize risks and build long-term trust with their clientele.
The Role of Emerging Technologies
The future of payment security is increasingly shaped by advancements in technology. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming central to identifying and preventing fraudulent activities. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of transaction data in real time, identifying patterns that may indicate fraud or other security threats. These systems can adapt to new tactics used by cybercriminals, continuously improving their ability to detect and block suspicious activity.
Blockchain technology is another emerging innovation that holds promise for enhancing payment security. Blockchain's decentralized nature makes it difficult for hackers to alter transaction data, providing an additional layer of security for digital payments. Blockchain-based payment systems can offer transparent, immutable records of transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring the integrity of financial data.
Additionally, quantum computing, while still in its early stages, has the potential to revolutionize encryption methods. Quantum computers are capable of solving complex mathematical problems at speeds that are currently unimaginable with classical computers. While this poses a potential threat to existing encryption standards, it also opens the door to developing new cryptographic techniques that could further strengthen payment security.
Challenges Facing Payment Security
Despite the advancements in payment security, several challenges remain. One of the most significant obstacles is the growing sophistication of cyberattacks. Cybercriminals are continually developing new techniques to bypass security systems and exploit vulnerabilities in payment networks. Phishing attacks, ransomware, and malware are just a few examples of the threats businesses face daily. As these attacks become more targeted and complex, companies must invest in more advanced security solutions to stay ahead of the curve.
Another challenge is balancing security with user experience. While additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication, improve protection, they can also add friction to the payment process. Consumers expect seamless and fast transactions, especially in e-commerce and mobile payments. Businesses must find ways to implement robust security measures without compromising the user experience, which can lead to abandoned transactions and lost sales.
The increasing reliance on third-party payment processors and platforms also poses risks. Many businesses outsource payment processing to external vendors, which can introduce vulnerabilities if those vendors do not meet stringent security standards. Ensuring that third-party providers comply with industry regulations and best practices is essential for maintaining the integrity of payment systems.
The Future of Payment Security
As the payment security landscape evolves, businesses will need to adopt a proactive approach to protect their customers and themselves from emerging threats. One key trend is the shift toward decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, which leverage blockchain technology to facilitate financial transactions without the need for intermediaries. DeFi systems offer enhanced transparency and security, but they also present new challenges, as they operate in a regulatory gray area in many jurisdictions.
Another trend is the increasing adoption of biometric security features in payment systems. As consumers become more comfortable with using facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice authentication, these methods will likely become standard in securing transactions. Biometric data is inherently difficult to replicate, making it an effective tool for preventing fraud.
In conclusion, payment security is a critical aspect of the modern financial ecosystem. As digital transactions continue to grow, businesses and consumers alike must prioritize security to protect sensitive information and maintain trust. The Payment Security Market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by innovations in AI, blockchain, and quantum computing. However, businesses must remain vigilant in the face of evolving threats, balancing the need for robust security with the demand for seamless user experiences. By staying ahead of the curve, companies can safeguard their payment systems and ensure a secure future for digital transactions.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)
About Us
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Read Our Other Reports: